About Us
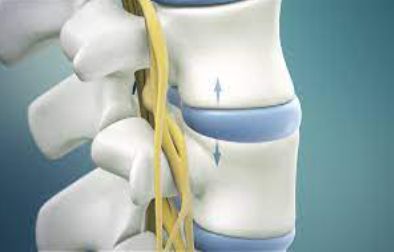
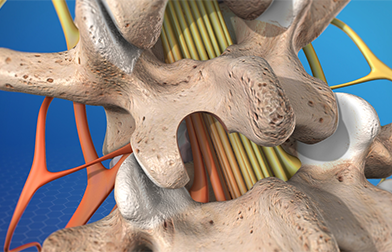
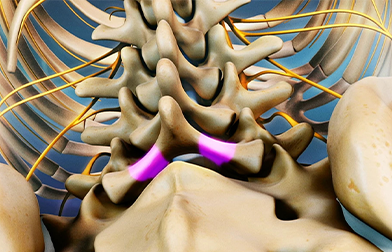
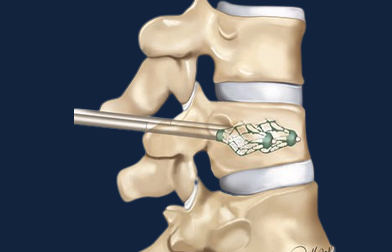
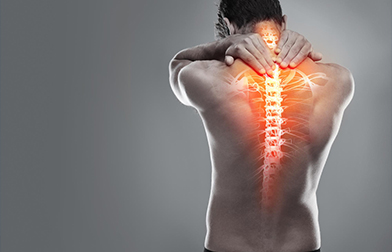
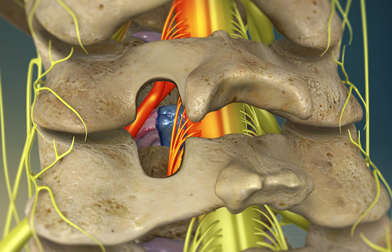
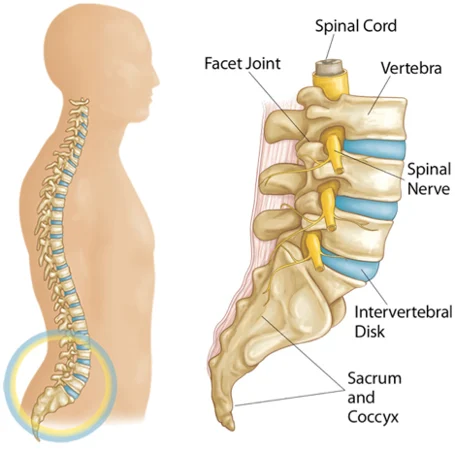
Maharaja Agrasen Hospital has one of the best spinal surgery unit in Rudrapur, Uttarakhand.It is a dedicated unit dealing with all simple and complex problems in spine.
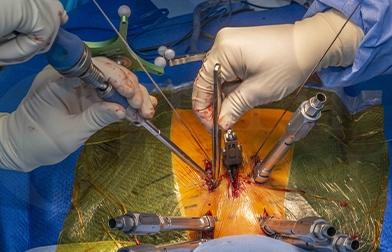
Our spine surgeon Dr. Naveen Agarwal M.B.B.S.(Gold Medalist), M.S(Ortho) FSS, FASSI, FAPSS specializes in Spinal Surgery and has been exclusively trained in Spinal Surgery. He is Consultant Orthopaedic and Spine Surgeon at Maharaja Agrasen Hospital. During his postgraduate days, Dr Naveen developed keen interest in spine surgery. As the training in orthopedics is insufficient to practice spine surgery, he has done fellowships from Park Clinic,Ganga Hospital Coimbatore Kolkata and Primus Superspecialty Hospital, New Delhi
Know More